Abstract
Alauddin Khilji, the ruler of the Delhi Sultanate in medieval India, faced numerous military challenges during his reign. These challenges included defending against Mongol invasions, suppressing internal rebellions, expanding the boundaries of the Sultanate, and overcoming logistical obstacles. To address these challenges, Khilji implemented significant military reforms, such as establishing a standing army, implementing strict disciplinary measures, introducing the branding system for horses, and constructing strategic forts. These reforms played a crucial role in consolidating his power, expanding the Sultanate's territory, ensuring the effectiveness of the armed forces, and strengthening the stability of the Delhi Sultanate. Khilji’s military strategies and decisions, including his aggressive expansionist policy and emphasis on defense, intelligence gathering, and resource utilization, contributed to his military successes and reshaped the socio-political dynamics of the Sultanate.

|
| An illustration of Alauddin Khilji. |
Keywords: economic policy, market control, price regulations, Medieval India, trade, commerce.
Introduction
Alauddin Khilji faced numerous historical challenges in the military sphere during his reign as the ruler of the Delhi Sultanate. When he ascended to power in 1296, the northern Indian region was marked by political fragmentation and external threats. One of the significant challenges Khilji confronted was the Mongol invasions. The Mongols, under the leadership of Genghis Khan and later his descendants, posed a persistent threat to the stability and sovereignty of the Delhi Sultanate. Khilji had to adopt strategies to defend against Mongol incursions, which often involved conducting military campaigns on multiple fronts and fortifying key border regions. Another significant challenge faced by Khilji was internal rebellion and regional uprisings. The Delhi Sultanate encompassed diverse regions and ethnic groups, and maintaining control over the vast empire was a complex task. Khilji had to quell several rebellions and uprisings, particularly in regions where the authority of the central administration was contested. These internal challenges required military action and strategic planning to suppress revolts and reestablish the Sultanate’s authority.
Khilji’s military endeavors were also influenced by his expansionist ambitions. He aimed to extend the boundaries of the Delhi Sultanate and bring more regions under his control. This drive for territorial conquest necessitated military campaigns against various kingdoms and principalities, which often involved facing well-entrenched armies and defensive structures. Khilji had to develop tactics and strategies to overcome the resistance offered by these regional powers, making careful calculations to ensure successful military outcomes. Moreover, logistical challenges posed another obstacle for Khilji. The vastness of the empire required efficient transportation and supply systems to sustain his military campaigns. Maintaining a well-equipped and provisioned army over long distances was a logistical feat that demanded careful planning and organization. Khilji had to overcome these challenges to ensure the mobility and effectiveness of his military forces. Alauddin Khilji faced numerous challenges in the military sphere during his reign. These challenges included defending against Mongol invasions, suppressing internal rebellions, expanding the boundaries of the Sultanate, and overcoming logistical obstacles. Khilji had to navigate a complex historical context marked by political fragmentation and external threats. Successfully addressing these challenges required strategic planning, military prowess, and efficient logistical systems. Despite the difficulties, Khilji’s military achievements played a crucial role in consolidating his power and expanding the territorial reach of the Delhi Sultanate during his reign.
Research Objectives
The objectives of this study are to examine the historical context and challenges faced by Alauddin Khilji in the military sphere, analyze his specific military reforms and their objectives, evaluate the effectiveness and impact of these reforms on the stability and expansion of the Delhi Sultanate, assess the strategic military decisions and their role in achieving successes, investigate the organizational structure and logistical advancements in Alauddin Khilji’s military administration, explore the use of innovative military tactics and technologies and their influence on battlefield outcomes, and study the relationship between Alauddin Khilji’s military reforms and the socio-political dynamics of the Delhi Sultanate.
Objectives in Points:
- Explore the background and the problems that Alauddin Khilji encountered in the army sector.
- Detail his particular military reforms along with their aims.
- Measure the degree of success of these reforms through their contribution to the stability and growth of the Delhi Sultanate.
- Review the military strategies undertaken and their contribution to victories.
- Look into the changes and the improvements of the organization and administration of Khilji’s army.
- Understand how the new military tactics and inventions changed the winning of battles.
Research Methodology
The research methodology employed in this study is historical in nature. It involves analyzing primary and secondary sources, such as historical texts, documents, and artifacts, to understand and interpret the events and context surrounding Alauddin Khilji’s reign as the ruler of the Delhi Sultanate.
Discussion
Alauddin Khilji, the renowned ruler of the Delhi Sultanate in medieval India, implemented significant military不说 System: military reforms with specific objectives in mind. His reforms aimed to strengthen the military capabilities of his empire, enhance centralized control, ensure effective administration, and secure his territorial conquests. One of the key military reforms implemented by Alauddin Khilji was the establishment of a highly organized and efficient standing army. He created a permanent military force known as the “New Standing Army” or the “Corps of Forty Thousand.” This standing army consisted of well-trained and disciplined soldiers who were paid regular salaries by the state. By maintaining a standing army, Alauddin Khilji aimed to ensure a quick response to any internal or external threats to his rule and maintain a constant state of readiness. To bolster the strength and effectiveness of his army, Khilji introduced strict measures to ensure discipline and loyalty among the soldiers. Harsh penalties were imposed for disobedience or negligence, and any signs of disloyalty or insubordination were dealt with severely. These measures aimed to create a strong sense of discipline, obedience, and loyalty within the military ranks, thereby enhancing the overall effectiveness of the armed forces.
Another important military reform introduced by Alauddin Khilji was the implementation of a system known as the “Dagh” or branding system. Under this system, horses belonging to the soldiers were branded, and their numbers and details were recorded by the state. This system facilitated efficient administration and helped in the identification and management of the cavalry. It also served as a means to prevent corruption and unauthorized use of state resources. In addition to these internal military reforms, Alauddin Khilji also implemented strategic measures to secure his borders and protect his territories. He constructed a network of forts and fortifications along the vulnerable frontiers of his empire. These forts provided strong defensive positions and acted as deterrents against enemy incursions. Moreover, Khilji implemented a policy of maintaining a strong cavalry force capable of conducting rapid raids and counterattacks, thereby deterring potential adversaries and expanding his own influence. Alauddin Khilji’s military reforms were aimed at centralizing control, enhancing military strength, ensuring discipline and loyalty, and securing his empire. These reforms played a crucial role in establishing Khilji as a powerful ruler and strengthening the Delhi Sultanate during his reign. The standing army, strict disciplinary measures, branding system, and fortifications all contributed to the military might and stability of his empire, enabling him to effectively govern his territories and defend against external threats.
The military reforms implemented by Alauddin Khilji had a significant impact on the stability and expansion of the Delhi Sultanate. These reforms were aimed at strengthening the military capabilities of the empire and ensuring its territorial integrity. One of the key aspects of Khilji’s military reforms was the focus on professionalization and discipline within the army. He introduced strict codes of conduct and discipline among the soldiers, emphasizing loyalty and obedience to the Sultan. This contributed to a more cohesive and disciplined military force, capable of executing orders efficiently and effectively. The professionalization of the army played a crucial role in enhancing the stability of the Delhi Sultanate by instilling a sense of unity and discipline among the troops. Khilji also introduced significant changes in the recruitment and organization of the military. He established a standing army known as the “New Order” or “Dagh,” consisting of experienced and well-trained soldiers. This standing army was paid regular salaries, provided with adequate provisions, and given land grants as rewards for their service. This systematic approach to recruitment and compensation ensured a reliable and loyal military force, which could be readily deployed to defend the empire and undertake offensive campaigns. Another notable military reform was the introduction of a strategic fortification system. Khilji constructed a network of strong fortresses, particularly along the empire’s borders, to protect against external invasions and maintain territorial control. These forts provided a strong defensive line and acted as bases for launching military operations. The fortification system played a crucial role in enhancing the stability of the Delhi Sultanate by deterring potential invaders and reinforcing the Sultanate’s control over key regions.
Khilji’s military reforms contributed to the expansion of the Delhi Sultanate’s territory. The professionalization and effectiveness of the army, coupled with strategic planning, enabled successful military campaigns and territorial conquests. Khilji undertook several military expeditions, expanding the Sultanate’s control over regions such as Gujarat, Malwa, and Rajasthan. The military reforms played a vital role in facilitating these conquests, ensuring the Sultanate’s territorial expansion and further strengthening its position. Alauddin Khilji’s military reforms had a profound impact on the stability and expansion of the Delhi Sultanate. The emphasis on professionalization and discipline within the army, the establishment of a standing army, and the strategic fortification system enhanced the Sultanate’s military capabilities and safeguarded its territorial integrity. These reforms provided a more stable and reliable military force, capable of defending the empire and undertaking successful military campaigns. Overall, Khilji’s military reforms played a pivotal role in shaping the Delhi Sultanate’s stability and expansion during his reign.
Alauddin Khilji, the ruler of the Delhi Sultanate in medieval India, made strategic military decisions that played a pivotal role in achieving significant military successes during his reign. These decisions encompassed various aspects such as expansion, defense, intelligence gathering, and utilization of resources. One of the notable strategic military decisions made by Alauddin Khilji was his aggressive expansionist policy. Recognizing the importance of territorial conquests for establishing and maintaining political power, Khilji launched military campaigns to expand the boundaries of his empire. He successfully captured and annexed regions like Gujarat, Malwa, and Ranthambore, thereby enlarging the territory under his control. This expansionist policy not only increased his realm but also enhanced his military resources, including manpower, wealth, and strategic locations.
Another significant strategic decision made by Khilji was his emphasis on strengthening the defense of his empire. He recognized the importance of fortifications in protecting his territories from external threats. Khilji invested in the construction and renovation of forts and fortifications, particularly along vulnerable frontiers. These fortified structures provided secure defensive positions and served as deterrents against enemy invasions. The defense-oriented approach of Khilji’s military strategy helped in safeguarding his territories and maintaining stability within his empire. Alauddin Khilji also displayed strategic acumen in gathering military intelligence. He established a sophisticated intelligence network that monitored internal and external developments. This network enabled him to gather vital information about rival kingdoms, their military strength, and their political alliances. By staying well-informed, Khilji was able to anticipate potential threats and devise appropriate strategies to counter them effectively. The intelligence-gathering efforts of Khilji’s administration played a crucial role in shaping his military decisions and ensuring the success of his military campaigns.

|
| Khilji in war front, an AI image |
Khilji’s effective utilization of resources was another key aspect of his strategic military decisions. He recognized the significance of a strong and well-equipped army in achieving military successes. Khilji focused on building a formidable cavalry force, known as the “Chaghtai Mashaikh,” which comprised skilled horsemen. This cavalry played a vital role in swift maneuvering, raiding enemy territories, and providing tactical advantages during battles. Khilji’s ability to mobilize and deploy his resources efficiently contributed to the overall effectiveness of his military campaigns. Alauddin Khilji’s strategic military decisions played a crucial role in his military successes. His aggressive expansionist policy, emphasis on defense and fortifications, intelligence-gathering efforts, and effective utilization of resources all contributed to his achievements on the battlefield. These strategic decisions enabled him to expand his empire, defend his territories, gather crucial intelligence, and deploy his military resources effectively. Alauddin Khilji’s astute military strategies and decisions were instrumental in establishing his reputation as a formidable ruler and ensuring the military prowess of the Delhi Sultanate during his reign.
Alauddin Khilji’s military administration during the medieval period in India exhibited notable organizational structure and logistical advancements that contributed to the efficiency and effectiveness of his armed forces. The organizational structure of Khilji’s military administration was characterized by a hierarchical system. The army was divided into different units, each headed by a commander or officer. These units included cavalry, infantry, and artillery divisions. Khilji placed great emphasis on discipline and strict military hierarchy. He appointed trusted commanders who were loyal to him and granted them significant autonomy in managing their respective units. This centralized command structure enabled swift decision-making and efficient coordination of military operations. In terms of logistical advancements, Alauddin Khilji implemented several measures to ensure the smooth functioning of his military administration. One significant logistical advancement was the establishment of an efficient supply chain system. Khilji recognized the importance of maintaining a well-provisioned army and implemented measures to ensure a steady flow of resources to his troops. He established granaries and storehouses in strategic locations, which stored ample food supplies and provisions for his soldiers during military campaigns. This logistical infrastructure enabled his forces to operate in remote regions without facing severe shortages.
Khilji also introduced reforms in the management of military finances. He established a treasury system that efficiently handled the revenue generated from his empire. This revenue was allocated to support the military’s needs, including the payment of salaries to soldiers, procurement of weapons and equipment, and maintenance of infrastructure. The financial reforms implemented by Khilji ensured a stable source of funding for his military administration, allowing for sustained military operations and the overall well-being of his armed forces. Another notable logistical advancement was the establishment of efficient communication networks. Khilji recognized the importance of timely and accurate information dissemination, both within his military administration and between different regions of his empire. He established a system of messengers and couriers who carried vital messages, orders, and reports between commanders, garrisons, and the central administration. This communication network facilitated swift decision-making, coordinated military movements, and ensured effective response to emerging situations. In addition to the organizational structure and logistical advancements, Alauddin Khilji’s military administration also focused on the training and professional development of his soldiers. He invested in military training institutions, where soldiers received rigorous training in various aspects of warfare. This emphasis on training improved the skills and combat readiness of his troops, enabling them to perform with proficiency on the battlefield.

|
| Siri Fort, located in New Delhi, was constructed under Alauddin Khilji to protect the city from Mongol invasions. |
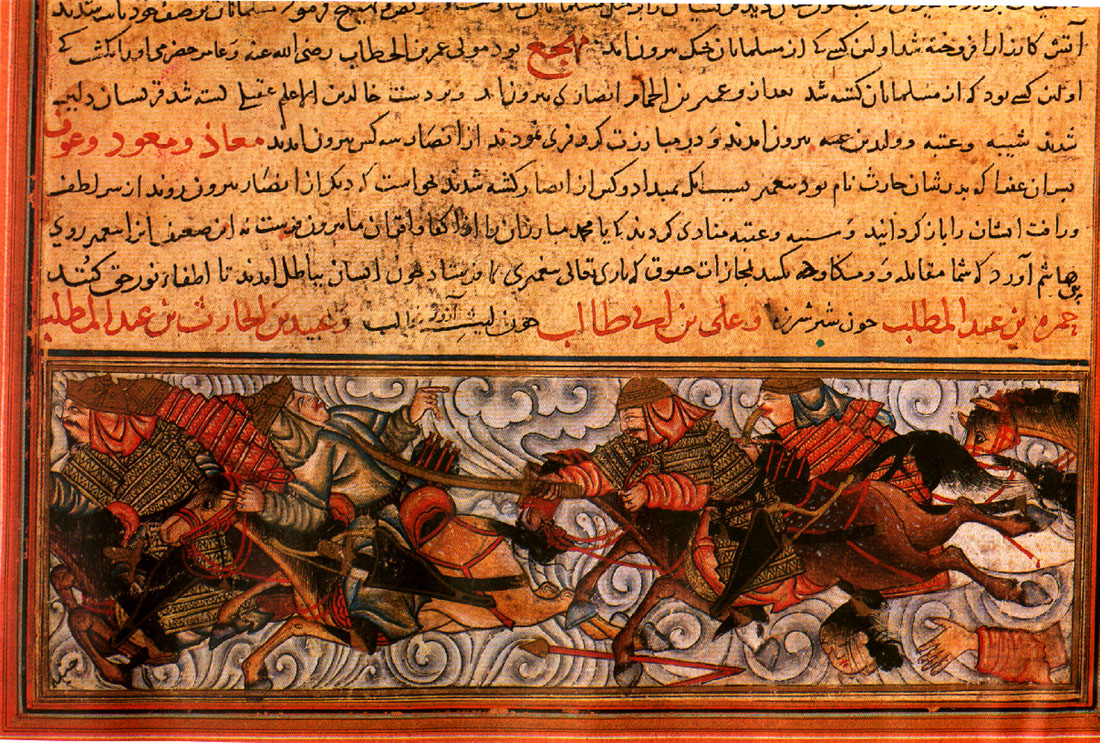
|
| Medieval battle depiction adaptable to Khilji campaigns |

|
| Ranthambore siege visualization |
The military reforms implemented by Alauddin Khilji had a profound impact on the socio-political dynamics of the Delhi Sultanate. These reforms not only enhanced the military capabilities of the empire but also played a significant role in consolidating Khilji’s power and reshaping the socio-political landscape. One key aspect of the relationship between Khilji’s military reforms and the socio-political dynamics was the strengthening of central authority. The establishment of a professional standing army and the implementation of strict discipline contributed to the consolidation of the Sultan’s power. The military reforms ensured that the army remained loyal and obedient to the Sultan, enhancing his control over the empire. This consolidation of central authority enabled Khilji to exert greater influence over the socio-political dynamics of the Delhi Sultanate and establish a more centralized governance structure. Khilji’s military reforms had a direct impact on the relationship between the ruling elite and the military. The establishment of the “New Order” and the provision of regular salaries and rewards created a sense of loyalty and dependence on the Sultan. The professionalization of the army under Khilji’s reforms reduced the influence and autonomy of regional military commanders and local power centers. This shift in power dynamics increased the Sultan’s control over the military and further solidified his position as the ultimate authority in the socio-political landscape.
The military reforms also had implications for the relationship between the Sultanate and the general populace. The fortification system and the effectiveness of the army instilled a sense of security and stability among the people. This contributed to social cohesion and reinforced the authority of the Sultanate. Additionally, the successful military campaigns and territorial expansion resulting from the reforms created a sense of pride and legitimacy for the Sultan’s rule. The military successes and the perception of a strong empire under Khilji’s leadership bolstered his legitimacy and support from the population. However, the socio-political dynamics were not without challenges. The consolidation of power in the hands of the Sultan and the centralization of authority led to a certain degree of resentment among regional elites and nobles. Some segments of society, particularly those whose influence was curtailed by the reforms, may have felt marginalized or threatened by the Sultan’s control over the military. This tension between central authority and regional power centers remained a constant feature of the socio-political dynamics during Khilji’s reign.
Alauddin Khilji employed innovative military tactics and technologies that had a significant influence on battlefield outcomes during his reign in medieval India. One notable military tactic used by Khilji was the concept of “Guerilla Warfare.” He understood the advantage of surprise attacks and hit-and-run tactics against larger and more conventional armies. Khilji’s forces, consisting of skilled horsemen, utilized their mobility and knowledge of the terrain to launch swift and unexpected attacks on the enemy. This strategy disrupted the enemy’s formations, created confusion, and allowed Khilji’s forces to inflict heavy casualties before retreating to safety. Guerilla Warfare tactics provided Khilji with a tactical edge and played a crucial role in his military successes. Khilji also embraced innovative technologies to enhance his military capabilities. One such technology was the use of advanced artillery. Khilji introduced powerful siege engines, such as catapults and trebuchets, which provided his army with the ability to breach fortified enemy positions. These artillery weapons allowed Khilji’s forces to inflict significant damage to enemy defenses, enabling successful sieges and conquests. The deployment of advanced artillery technology enhanced the effectiveness of Khilji’s military campaigns and gave him a decisive advantage over his adversaries.
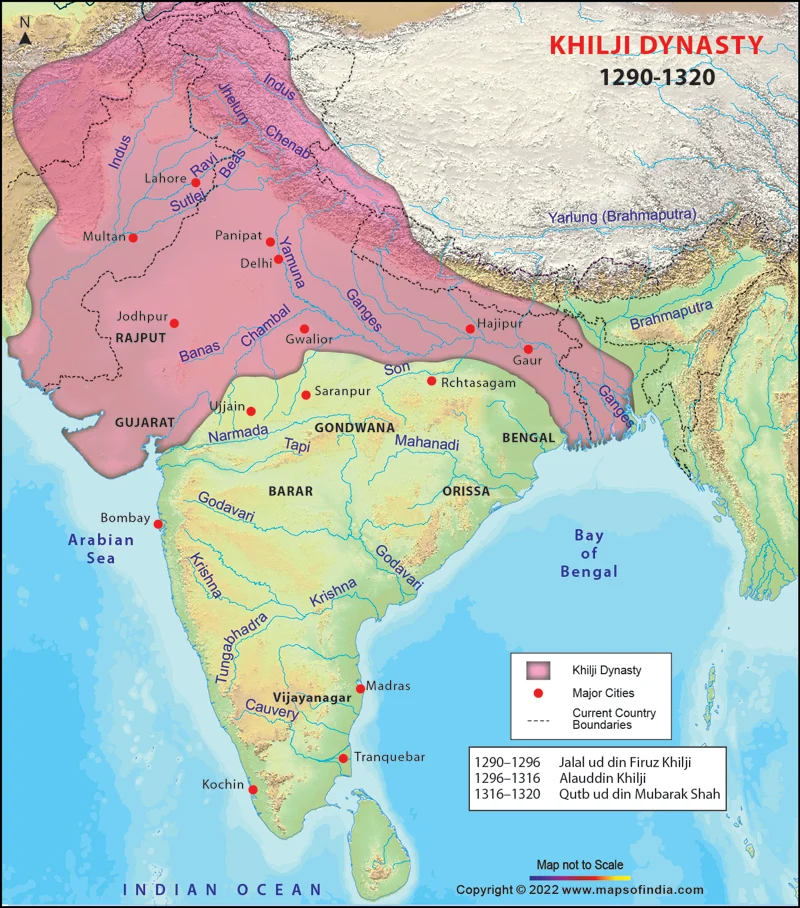
|
| Map showing Khilji expansions 1290-1320 |
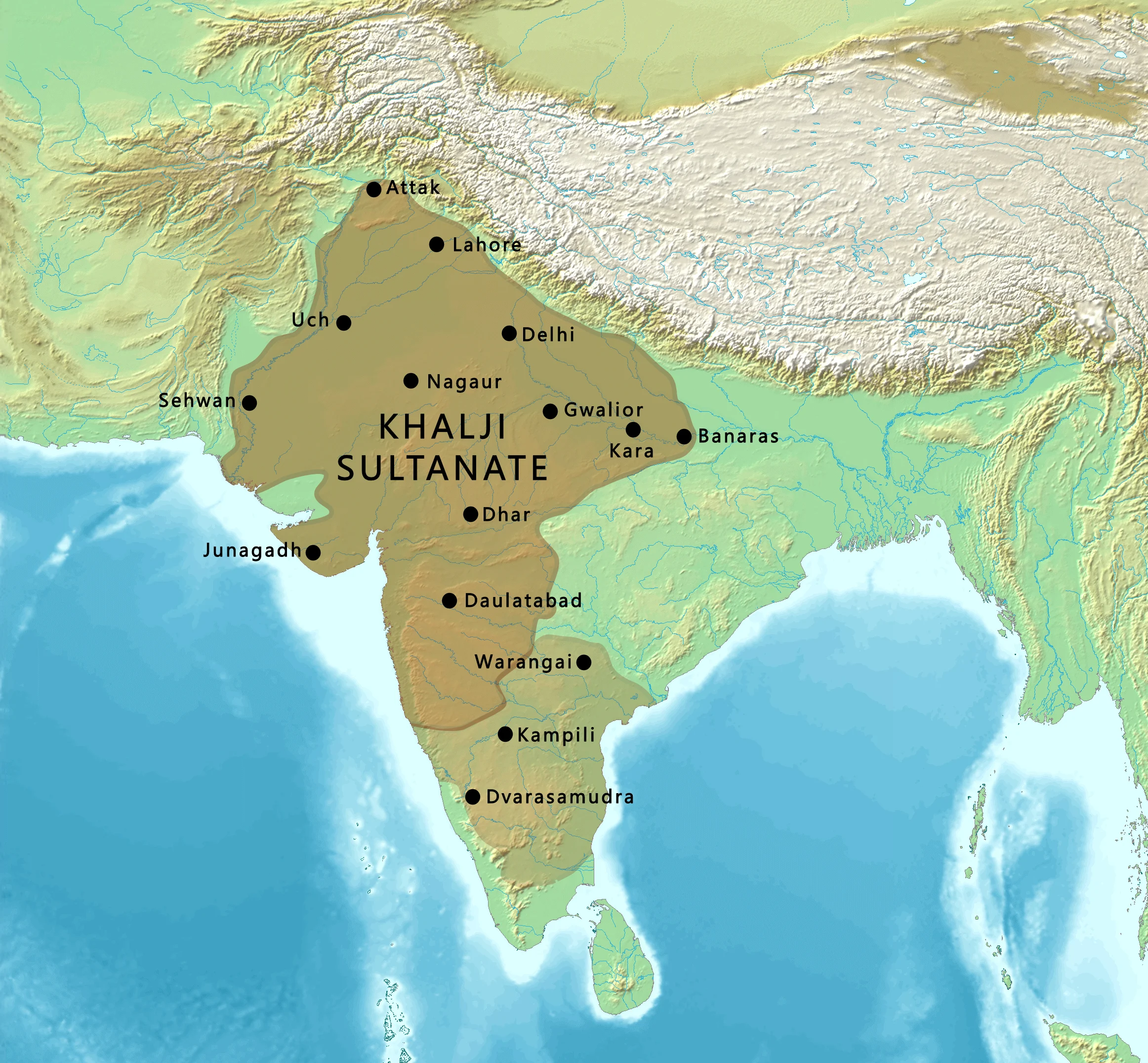
|
| Detailed Khalji Sultanate boundaries |
Khilji employed psychological warfare tactics to intimidate and demoralize his enemies. He understood the importance of instilling fear and uncertainty among his opponents. One of his tactics involved displaying the severed heads of defeated enemies, particularly in front of fortified cities, to create a sense of terror and discourage resistance. This psychological warfare strategy aimed to weaken the enemy’s resolve, lower morale, and facilitate easier conquests. Khilji’s use of psychological tactics contributed to his military successes by creating a psychological advantage for his forces. Khilji emphasized the importance of intelligence gathering and reconnaissance. He employed spies and scouts to gather information about the enemy’s strengths, weaknesses, and battle plans. This intelligence allowed him to devise appropriate strategies and make informed decisions on the battlefield. By having a clear understanding of the enemy’s movements and intentions, Khilji could effectively position his forces and exploit any vulnerabilities, leading to favorable battlefield outcomes.
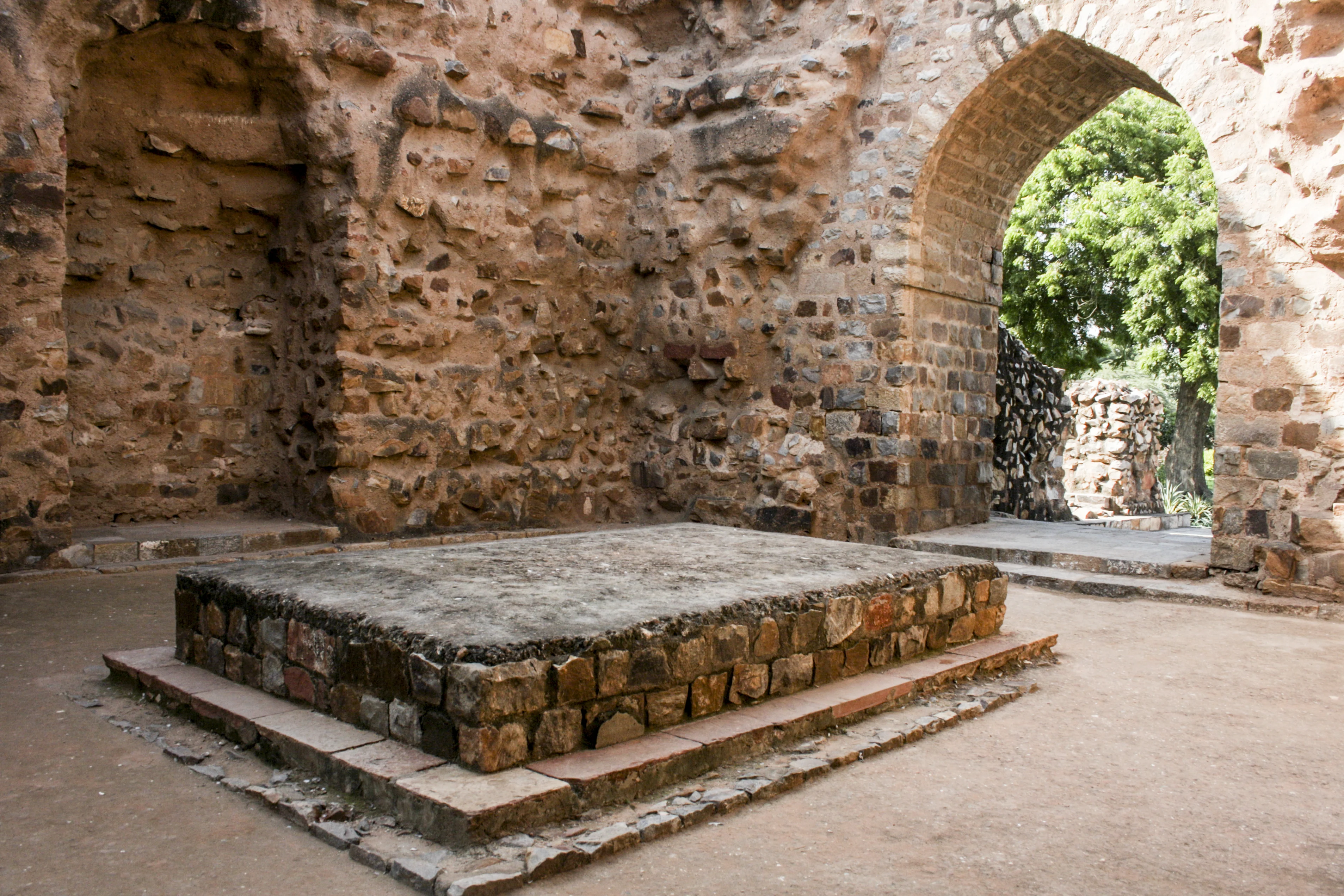

|
| Alauddin Khilji Tomb (located in the central room of the southern wing of the L-shaped madrasa in Qutb Minar complex, Delhi) |
Conclusion
Alauddin Khilji’s reign as the ruler of the Delhi Sultanate in medieval India was marked by numerous military challenges and strategic decisions that shaped the empire’s stability, expansion, and overall military capabilities. Khilji successfully navigated a complex historical context characterized by political fragmentation, external threats, internal rebellions, and logistical challenges. His military reforms, including the establishment of a standing army, strict disciplinary measures, fortification systems, and logistical advancements, played a crucial role in consolidating his power, expanding the Sultanate’s territory, and maintaining control over diverse regions. These reforms enhanced the military might and stability of the Delhi Sultanate, enabling Khilji to defend against Mongol invasions, suppress internal rebellions, and undertake successful military campaigns. Khilji’s strategic decisions, such as aggressive expansionist policies, emphasis on defense and fortifications, intelligence gathering, and resource utilization, contributed to his military successes and reshaped the socio-political dynamics of the empire. The centralization of authority, the strengthening of the ruling elite’s relationship with the military, and the sense of security and legitimacy among the populace were all outcomes of his military reforms. Alauddin Khilji’s astute military strategies, innovative tactics, and effective administration left a lasting impact on the Delhi Sultanate, establishing him as a formidable ruler and contributing to the empire’s stability and expansion during his reign.

|
| Khilji, an AI image |
References
- Sundararaj, S. (1980). Early Muslim Conquests of Tamil Country. The Quarterly Journal of the Mythic Society.
- Joshi, P. S. (1975). A Study of the Religious Aspect of the Period of Chhatrapati Shivaji. Chhatrapati Shivaji: Coronation ... University of Bombay.
- Ramya, S. (2007). The Many Lives of a Rajput Queen. Seattle and London: University of Washington Press.
- Amma, T. A. S. (1999). Geometry in Ancient and Medieval India. Google Books.
- Nizami, K. A. (1957). Some Aspects of Khānqah Life in Medieval India. Studia Islamica.
- Ray, A. (2016). Towns and Cities of Medieval India: A Brief Survey. Google Books.
- Basham, A. L. (1976). The Practice of Medicine in Ancient and Medieval India. Asian Medical Systems: A Comparative Study.
- Mehta, J. L. (1979). Advanced Study in the History of Medieval India. Google Books.
- Habib, I. (2002). Essays in Indian History: Towards a Marxist Perception; with, the Economic History of Medieval India: A Survey. Google Books.
- Niazi, G. S. K. (1992). The Life and Works of Sultan Alauddin Khalji.
- Kaur, J. (2019). Character and Achievements of Alauddin Khilji. International Journal of History.
- Bhat, R. M. (2022). An Analytical Study of the Kushan Rule in Kashmir. Journal of Psychology and Political Science (JPPS), 2(04), 9-14, ISSN 2799-1024.
- Bhat, R. M., & Rajeshwari, R. (2022). Social Status of Women in Early Kashmir. Journal homepage: www.ijrpr.com, ISSN 2582-7421.
- Bhat, R. M. (2022). Women Exploitation in the Contemporary India: Importance of Media to Impede it. Journal of Women Empowerment and Studies (JWES), 2(02), 27-30, ISSN 2799-1253.
- II Ala-ud-din, S. de Delhi. (n.d.). Alauddin Khilji.
- Ali, M. B., & Laskar, B. A. S. (n.d.). Futuhus Salatin and Tarikh-i-FirujShahi; Two Great Works of the Sultanate Period, A Critical Study.
- Susilo, J., & Ridwan, M. (n.d.). Telaah Historis Kebijakan Ekonomi Sultan Alauddin Khalji.
- Singh, A. (2018). Origin and Ruling Period of Delhi Sultanate. International Journal of Academic Research.
- Padmini, R. (n.d.). Rani Padmini. en.bharatpedia.org.
- Kidwai, S. (2000). Ziauddin Barani: The Khaljis in Love (Persian). Same-sex Love in India: Readings from Literature and ....
- Khilji, J. (2011). 1290-96 CE. A Comprehensive History of Medieval India: Twelfth to ....
- Chandra, S. (2007). History of Medieval India: 800-1700. academia.edu.
- Habib, I. (1992). Medieval India. academia.edu.
- Chandra, S. (2005). Medieval India: From Sultanat to the Mughals Part-II. Google Books.
- Ali, D. (2004). Courtly Culture and Political Life in Early Medieval India. Google Books.
- Ahmed, Z., Aziz, S., Alauddin, S., et al. (2020). In Vitro Cytotoxic and Antimicrobial Activities of Erythrina suberosa (Roxb) Bark. Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmacology.
- Khalji, A. (n.d.). Alauddin Khalji.
- Bhansali, S. L. (2018). Padmaavat.
- Gupta, N. (2021). Ala-ud-Din's Deccan Policy.
- Habib, M. (1931). The Campaigns of Ala-ud-din Khilji. In Politics and Society During the Early Medieval Period....
- Bhat, R. M. (2021). Reign of Utpala Dynasty with Special Reference to Avantiverman (855-883 AD): His Irrigation Works and Agricultural Development-A Historical Study. International Journal of Agriculture and Animal Production (IJAAP), 1(02), 10-16, ISSN 2799-0907.
- Bhat, R. M. (2023). Dr. Bhim Rao Ambedkar’s Advocacy of Women Rights. MORFAI JOURNAL, 2(4), 730-736.
- Bhat, R. M. (2022). Dr. BR Ambedkar’s Views on Religion and Conversion to Buddhism: An Analytical Study. Journal of Legal Subjects (JLS), 25-31, ISSN.
- Fuller, A. R., & Khallaque, A. (1967). The Reign of Alauddin Khilji, Translated from Zia ud-din Barani's Tarikh-i-Firuz Shahi. Calcutta: Pilgrim Publishers.
- Habib, I. (1984). The Price Regulation of Alauddin Khilji: A Defence of Barani. IESHR.
- Habib, M. (1933). Campaigns of Alauddin Khilji, Being Trs. of Amir Khusrau's Khazain-ul Futub. Bombay.
- Bhat, R. M. (2022). Ghandian Phase: Mahila-Samitis and the Role of Women in the Indian National Movement. Journal of Women Empowerment and Studies (JWES), 2(01), 26-29, ISSN 2799-1253.
- Bhat, R. M. (2023). The Ghadar Movement: Igniting the Flame of Freedom in India. International Journal of Educational Review, Law And Social Sciences (IJERLAS), 3(4), 1123-1131.
- Bhat, R. M. (2022). Legacy of Buddhism in Kashmir. Journal of Psychology and Political Science (JPPS), 2(03), 23-30, ISSN 2799-1024.
- Bhat, R. M., Rajan, P., & Gamage, L. (2023). Redressing Historical Bias: Exploring the Path to an Accurate Representation of the Past. Journal of Social Science, 4(3), 698-705.
- Farid, G. S. (1976). Hitherto Unknown Silver Tankah of Sultan Alauddin Ali Mardan Khilji, 607-610 AH. Journal of the Asiatic Society.
- Khilji-Muhammad-bin-Tughlaq, A., & Tughlaq, F. (1989). BHI-12 History of India from 1206 AD to 1707 AD Syllabus. Europe.
- Roy, B. (2018). Visual Grandeur, Imagined Glory: Identity Politics and Hindu Nationalism in Bajirao Mastani and Padmaavat. Journal of Religion & Film, 22(1).
- Allawi, M., & Ahmed, G. S. (2022). Political and Administrative Life in the Countries that Ruled the Deccan Region (4-10 AH/10-15 AD). Journal of Surra Man Raa.
- Baswal, M. (2021). Many Histories of Ranthambore Fort, Rajasthan.
- Bhat, R. M. (2022). Queen Yasovati: A Descriptive Study on Her Leadership in the Kingdom of Kashmir. Journal of Psychology and Political Science (JPPS), 2(05), 11-17, ISSN 2799-1024.
- Hamood, R. R. (2011). Tank Irrigation by Muslim Case Study (Hauz Khas): A Historico–Geographical Study. Diyala Journal of Human Research, 2(1).
- Phe, R. R. H. (2011). Tank Irrigation by Muslim Case Study (Hauz Khas): A Historico–Geographical Study. مجلة ديالى للبحوث الانسانية, 2(1).
- Mursalin, K. R. (2018). Padmaavat (2018): A Successful Adaptation or a Tool for Propagating Grandeur of a Particular Sect. Available at SSRN 3665135.
- Kumar, N., & Navy, I. (n.d.). A Study of Various Reforms During Tughlaq Period. Retrieved from irtjournal.com.
- Bhat, R. M. (2022). Cultural Heritage of Early Kashmir-A Study. International Journal of Educational Review, Law And Social Sciences (IJERLAS), 2(4), 571-576.
- Bhat, R. M., & Rajeshwari, R. (2022, December). Diasporic Culture and International Relations-A Historical Study. In International Conference on Health Science, Green Economics, Educational Review and Technology, 4, 41-46.
- Kumari, M. A. (n.d.). Alauddin Khilji Ki Rajpoiot Neeti 1296 se 1316 tak. Faizabad.
- Imam, F. A. (1988). Price and Wage Structure in Fourteenth Century Delhi. Proceedings of the Indian History Congress.
- Fuller, A. R., & Khallaque, A. (1869). The Reign of Alauddin Khilji. Manipal University Jaipur Repository.
- Bhat, R. M. (2021). Legacy of Buddhism in Kashmir. Journal of Language and Linguistics in Society (JLLS), 1(01), 13-20, ISSN 2815-0961.
- Bhat, R. M., & Rajeshwari, R. (2022). Judicial Administration in Madras Presidency from 1858 to 1862.
- Bhat, R. M. (2022). Source: Proceedings of the South Indian History Congress 38 (2018), 554-557.
- Bhat, R. M. (2022). Historical Review of Indian Constitution. Traditional Journal of Law and Social Sciences, 1(02), 100-110.
- Bhat, R. M., Silllalee, A., Kandasamy, L., Gamage, L., & Rajan, P. Exploring Bilhana's Contributions to Indian Historiography.
- Bhat, R. M. Historical Review of Neolithic Culture in Kashmir-A Case Study of Burzahama.
- Sharma, D. R. M. K., & Solanki, R. (n.d.). International Journal of Education & Applied Sciences Research (IJEASR). Retrieved from academia.edu.
- Prasad, D. (1929). A Silver Coin Struck in Nepal in the Name of Ala-ud-din Muhammad Shah Khilji. JASB Num. Supp.
- Pal, D. (1947). Ala'-ud-Din Khilji's Mongol Policy. Islamic Culture.
- Sharma, R. (1955). A Mediæval Experiment in Totalitarianism. Proceedings of the Indian History Congress.
- Page, P., & Temple, C. (n.d.). Indian Hi. § Tqry.
- Nahar, K. K. (2020). Padmaavat (2018): Practice of Power and Vision in Three Lead Characters Comparing with the Literature. Available at SSRN 3697588.
- Subrahmanian, N. (1994). Social and Cultural History of Tamilnad: AD 1336-1984.
- Singh, M. (1978). Medieval History of India. New Delhi: Vikas Publishing House.
- Aziz, A. A. (1999). Malik Kafur's Expedition to the. Journal of Indian History.
- Tewari, Y. (2008). In the Sultanate Period. Region in Indian History.
- Tomb, G. D. T. (n.d.). 4.3. Muhammad Bin Tughluq 55. Delhi Sutanate - AnVi OpenSource Knowledge Trust.
- Pande, R. (1986). Succession to the Throne in the Delhi Sultanate Some Observations. Proceedings of the Indian History Congress.
- Faruqui, M. D. (2009). Comparative Studies in Society and History.
- Baum, H. (n.d.). A Royal Pain: Tensions of Womanhood in Padmaavat. Comm-Entary Staff.